There is no doubt that we are living in the world of science and technology as well as innovation. The inclusion of innovation and technology has touched all the industries, and also the facets of life. When we talk of the display devices, a lot of development has gone into making the displays more advanced and vibrant in the contemporary scenario, especially the displays of wearable like smartwatches and fitness bands. The most advanced kind of display is the OLED display.
Well, this blog will not have a complete focus on the OLED display or technology, but on TFE or Thin Film Encapsulation, and why is it considered as the most advanced display technology going forward.
Some Insight into the Thin Film Encapsulation Technology
It is very common to see the people wearing smart wearable devices, and this trend will grow stronger ands stronger in the years to come. With the increase of wearable devices, flexible active-matrix OLEDs are seen as the next-gen display tech. To guarantee protection of flexible devices, conventional encapsulation methods are not appropriate as a result of their characteristic rigidity, and TFE is considered as the most promising tech.
TFE is based on a multi-layer film, formulated of alternating inorganic and organic layers. The inorganic layers are characteristically made of metal oxides and function as the barriers of moisture. These layers are almost tremendously good barriers, but they are mechanically inflexible and brittle. Furthermore, these layers alone would obviously present pinhole defects, that in the long run would let oxygen and water in. In normal TFE structures, organic planarization interlayers are employed, for improving the mechanical properties of the multilayer and to limit the water infusion through the pinholes.
The organic layers are frequently put by ink-jet printing, while or ALD can be used for the deposition of the inorganic layers, usually made of nitrides or oxides. These layers must be put at low temperature, deprived of damaging the OLED stack, which is underneath. If seamlessly integrated, TFE could allow truly lightweight, flexible, devices, entirely on the basis of plastics.
TFE is consequently a very intricate design, where each component has to be physically, chemically, mechanically and optically enhanced, for assuring more than a few years of lifetime to the OLED device, deprived of damages. From the point of view of material design, TFE is tremendously challenging and incessant research is on-going, in order to optimize both the inorganic and organic layers materials and the consistent deposition processes.
Coming to a Close
In the contemporary time, the application areas of the thin film encapsulation have increased, and what’s more it is used in the latest smartphones and smart wearables. Smartphones and smart wearables are owned by almost everyone, and the number is only growing.
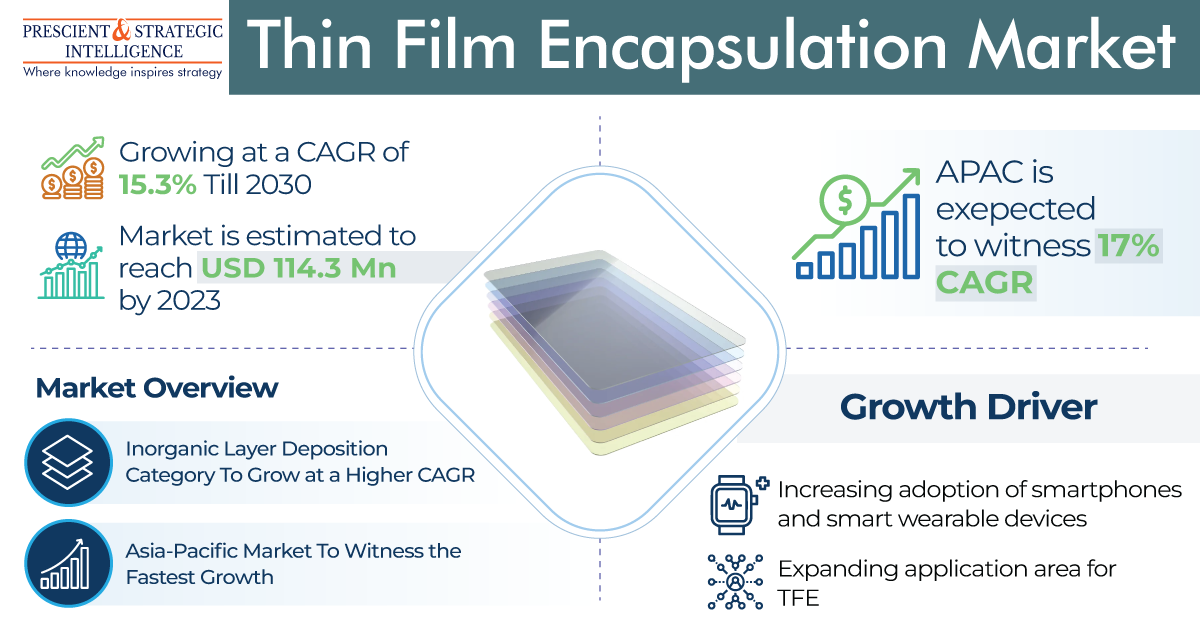
These are the main reasons why the demand for thin film encapsulation is on the rise, and it will reach a value of USD 310.4 million by the end of this decade.