Today’s automobiles are producing and transmitting huge quantities of data in order to execute advanced driver assistance systems, cameras and sensors, onboard diagnostics, smart safety systems, and in-vehicle-infotainment systems. Such in-vehicle networks need much quicker speeds than what has historically been possible utilizing buses like LIN, CAN/CAN-FD, PSI5, FlexRay, SENT, and CXPI networks.
Also, the need for better integration between vehicle subsystems is propelling fundamental architectural changes with a focus on scalable architectures and complex topologies, including gateways connected to a backbone.
Beyond the technical needs, such in-vehicle networks are also required to be cost-effective, light in weight, and work in rough conditions and extensive temperature ranges. They also require to be tremendously dependable, especially for systems made to protect the security of the passengers.
Automotive Ethernet answers all of these demands.
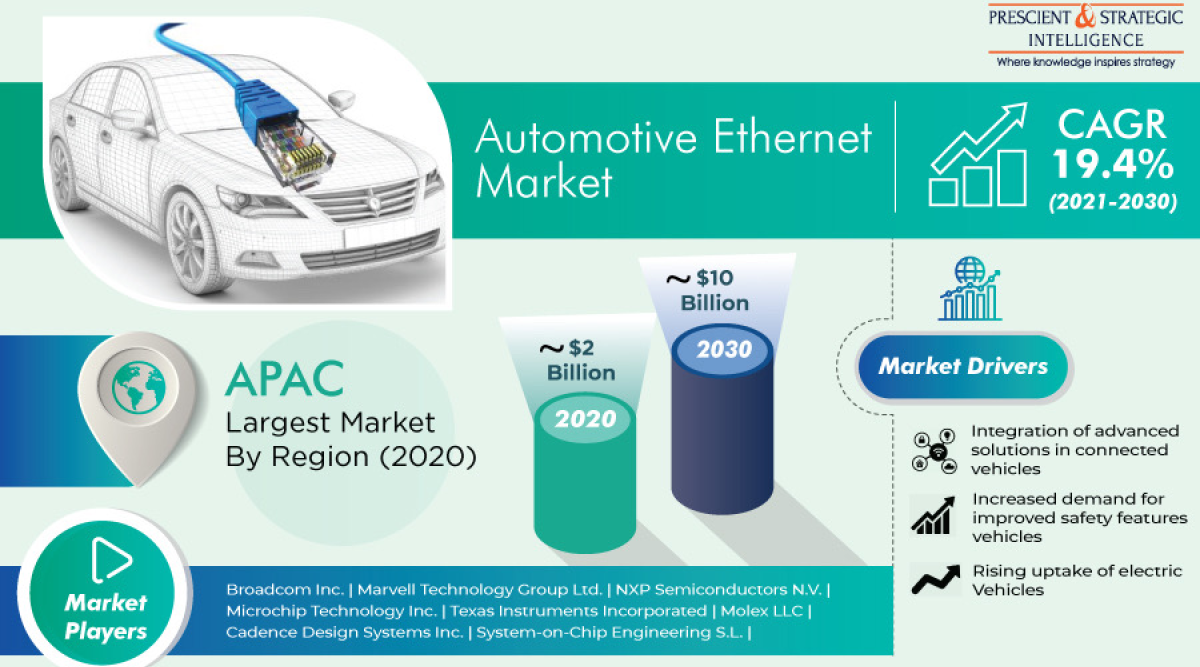
The automotive ethernet market is witnessing growth and is projected to reach USD 10 billion by 2030.
What is Automotive Ethernet?
Vehicle Ethernet is a low-latency, high-speed network physical layer. Vehicle Ethernet is based on recognized ethernet standards, and modified for use in automobiles. It utilizes a single pair of unprotected twisted cables for lightweight and low price.
It is made to permit the transfer of high volumes of information between in-vehicle modules to aid contemporary powertrain, ADAS, comfort, and infotainment systems. There are numerous different automotive ethernet standards, such as 10GBASE-T1, 100BASE-T1, and 1000BASE-T1, which can transfer information at speeds from 100 Mb/s to 10 Gb/s.
Benefits of Automotive Ethernet
In vehicles, automotive ethernet components provide numerous advantages, including:
High data rates allow high-speed, high-capacity data communications
- Low latency offers negligible delay for real-time systems such as ADAS
- High dependability with good noise immunity
- Light in weight, space-effective, and lucrative cabling
- Based on deep-rooted standards from reputable standards bodies
Moreover, automotive ethernet has been proven to meet the needs of both capacity and integration. For the purpose of achieving high data rates and reliability, automotive ethernet cables shall use PAM3/PAM4 modulation as opposed to nonautomotive Ethernet.
In the short term, however, automotive Ethernet can transport data approximately 100 times more rapidly than a bus and is better suited for future vehicle networks that will need to be capable of meeting their needs in terms of both performance and flexibility. The CAN, CANFD, LIN, and other networks are still relevant but they may prove less important in the next few years.
Automotive Ethernet Standards
As new workings for automotive Ethernet developed and speeds became quicker, standards establishments released new test and compliance needs that automotive makers and their suppliers should meet. To ensure the interoperability of hardware and the safe, predictable operation of the vehicle in different situations and working conditions, severe restraints are placed on noise, signal levels, and clock characteristics.
The testing methods specified by the standards, though deep-rooted for stationary Ethernet networks have made new design challenges for numerous automotive engineers familiar with working with slower serial buses like CAN and LIN.
Browse detailed report on Automotive Ethernet Market Size, and Business Strategies